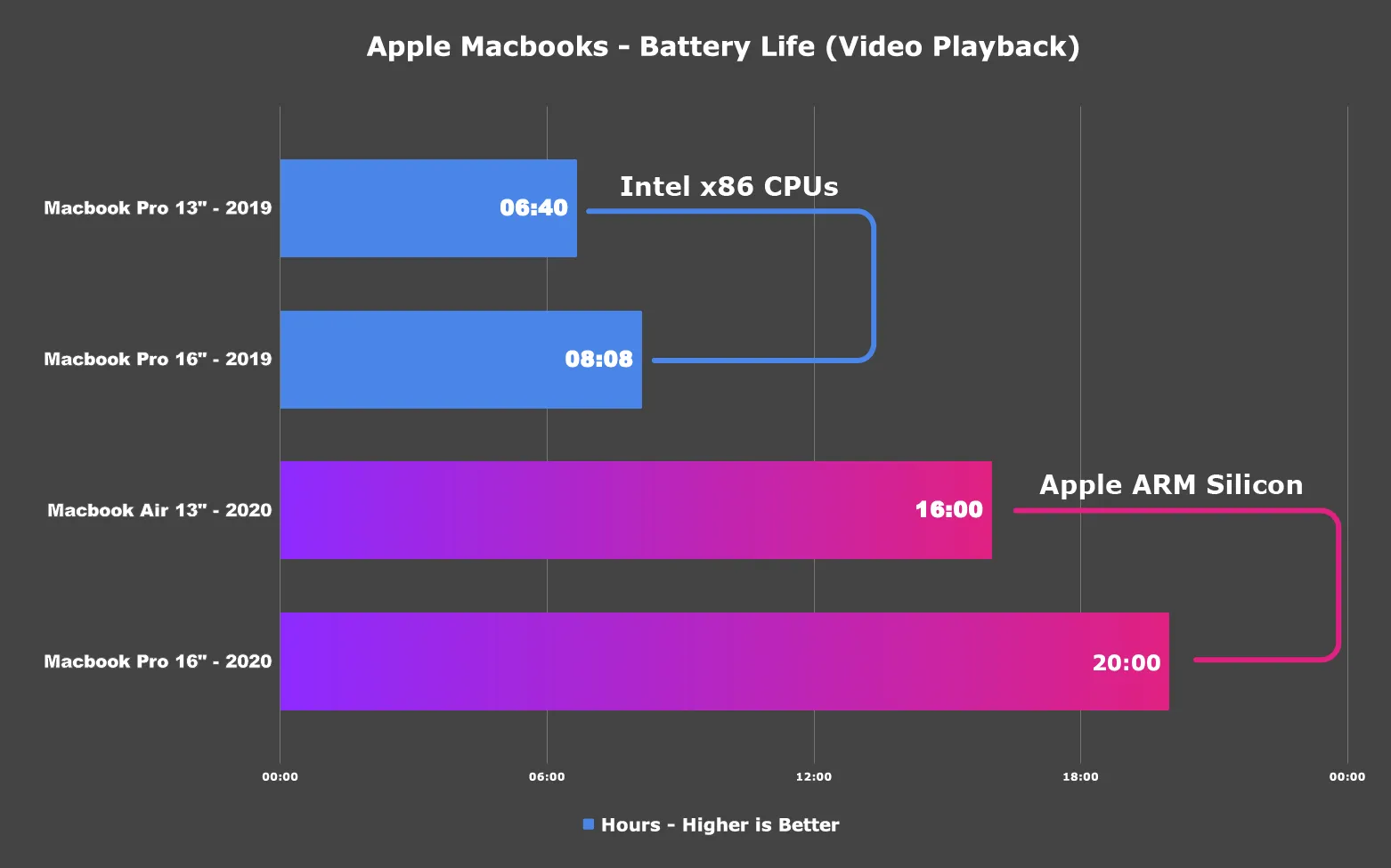
What is an ARM processor? How does a relatively slim laptop like the Apple Silicon powered laptops – provide hours and hours of battery life – there is ONE answer – ARM.
ARM aka Advanced RISC (Reduced Instruction Set) Machines. This architecture is responsible for all day battery life on mobile phones, laptops, tablets and embedded systems. Traditionally known for lower costs, lower power consumption and minimal heat generation.
The misconception remained that these particular processors architecture is meant for lower power devices – cut to 2023 – things have changed and how!
Attempting to explain this without getting technical will be tough – To contextualise this – there are two main architectures with respect to mainstream computer processing (laptop and desktop) – namely x86 and ARM.
X86 processors are the most common and prevalent ones available in the market – to put it simply – hardware components within an x86 framework function independently ( gpu, memory storage and the CPU itself). Most components will have separate controllers – these can be changed or upgraded without affecting overall functionality.
When it comes to the ARM architecture- it doesn’t need to have a separate “CPU” – the processing unit and all other controllers are on the same physical level – that is like an integrated circuit. Unlike x86 based computers – these ARM based chips aren’t interchangeable and are designed to be VERY application specific – what you would call a system on a chip (SOC).

With me so far? So x86 is more versatile, modular and vastly superior in terms of upgradability – whereas ARM is kind of limiting your “options” so to speak. So the natural conclusion that would pop in your head would be – x86 rocks & ARM is “meh” – not quiet.
Think of it this way – would it make more sense for a single person to travel a 2 km distance in a petrol guzzling 4×4 SUV or just take your motorbike.? Your answer to that question is what raised the need for reduced instruction set computing. You don’t need a shotgun to kill a fly.
So – the x86 processors come with more transistors, are larger, run hotter and are typically sensible in settings where you don’t care about the power budget being spent. ARM processors makes sense when you’re constantly looking over your back to see the power draw and figure out the most sensible instruction to give to the processor to accomplish its task as efficiently as possible. That’s not to say ARM processors can’t do high performance compute – they kind of need to be re-purposed to do the task which needs high performance compute.
Case in point is that – each ARM design is unique – unlike x86 processors ( trust me – regular desktop motherboards need a god damn overhaul). ARM doesn’t even sell processors – they just license you a chip design allowing you to manufacture it yourself.
So coming back to our premise – Why did Apple ditch Intel processors for their own ARM based “Apple Silicon”. Way back in 1990 – Apple was one of the founding partners for ARM – they even tried using it in products like “Newton” in 1993 ( first of its kind personal digital assistant).
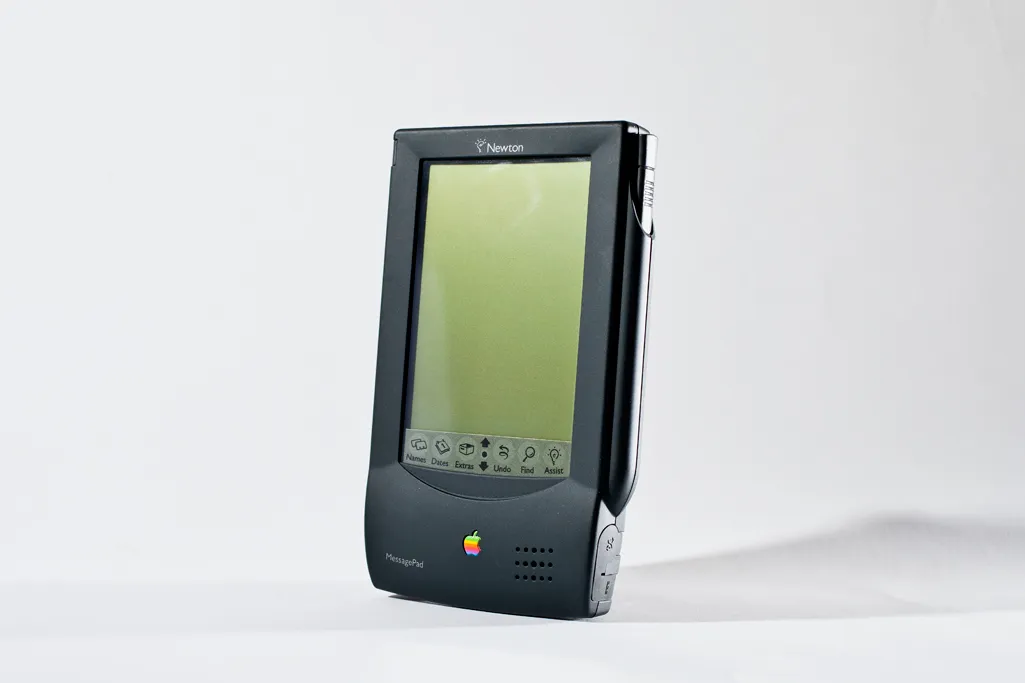

Apple struck gold when they started shipping iPods in 2001 – based on guess what – an ARM based processor. A music player doesn’t need a super powerful processor – it needs a processor that just sips power and does pre-defined tasks.
Years of improvements and innovation led to M1 based chips – which apart from having “benefits” save them a ton of money. So what is better here – ARM or x86 – the answer to that question my friend – remains – it depends on what you are going to use the processor for. So what do you think? Drop a comment let’s keep the conversation flowing.

Leave a Reply